Gardening questions may not have direct answers because gardening is a complex and multifaceted subject. There are many factors that can influence the success of a garden, including soil type, climate, sun exposure, water availability, and pest management. Additionally, different plants have different needs, and what works for one plant may not work for another.
Furthermore, gardening is a skill that requires practice and experience. There are often many different ways to achieve the same result, and what works best for one gardener may not work for another. As a result, gardening questions often require a more nuanced and personalized approach that takes into account the specific needs and circumstances of the gardener and their garden.
Finally, gardening is an ever-evolving field, and new research and techniques are constantly emerging. What was once considered the best practice may no longer be the case, and what works today may not work tomorrow. As a result, it is important to stay up-to-date on the latest gardening trends and information in order to achieve the best results in your garden.
Common Garden Questions
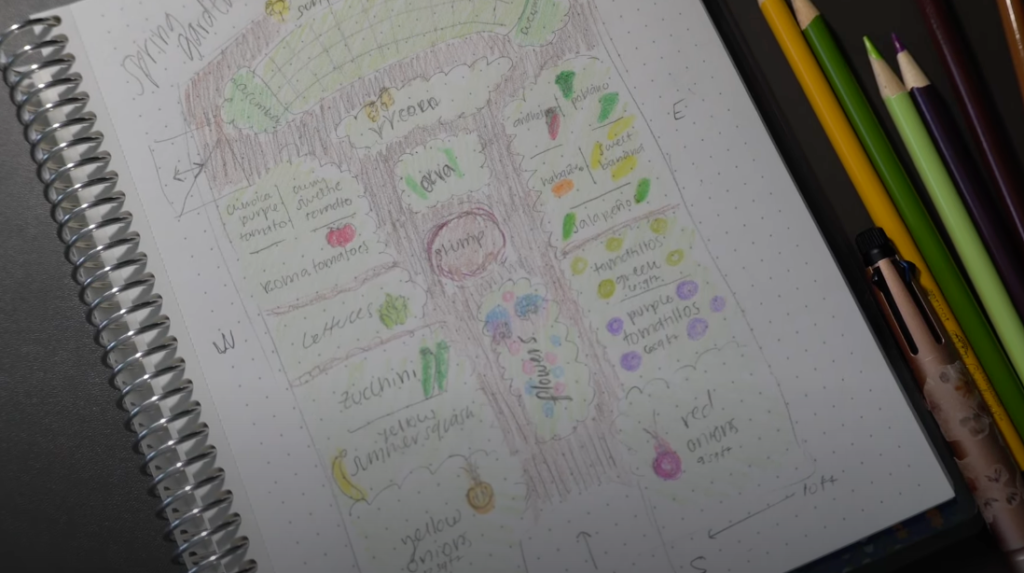
How do I design a garden layout?
Designing a garden layout is unique to every garden. However, there are a few steps to take that will help make the process easier.
- Assess your site: Start by assessing your site and considering factors such as sunlight, soil type, and drainage. This will help you choose plants that are appropriate for your site and arrange them in a way that maximizes their growth and beauty.
- Determine your goals: Consider what you want to achieve with your garden, such as growing vegetables, creating a wildlife habitat, or simply enhancing the beauty of your outdoor space.
- Make a plan: Sketch out a plan for your garden, using graph paper and a scale that allows you to accurately represent the size of your site. Decide on the shape and size of your garden beds, paths, and other features.
- Choose your plants: Choose plants that are appropriate for your site and your goals. Consider factors such as color, texture, and bloom time to create a visually appealing garden. Group plants together that have similar water, light, and soil requirements.
- Consider hardscaping features: Hardscaping features such as paths, walls, and benches can add structure and interest to your garden. Choose materials that complement the style of your home and garden.
- Create a focal point: Create a focal point in your garden, such as a sculpture or water feature, to draw the eye and add interest.
- Incorporate edibles: If you’re interested in growing vegetables or herbs, consider incorporating them into your garden design. This can add beauty and interest, as well as provide fresh produce for your table.
- Add finishing touches: Add finishing touches to your garden, such as mulch, decorative accents, and lighting, to complete the look and create a welcoming outdoor space.
For more information on garden layouts, read our article How to Layout a Garden Based on the Space Available.
Or watch our video about Balcony Gardening here.
What should I plant in my garden?
In general, you should plant vegetables, flowers, or other plants in your garden that you enjoy eating or looking at. However, there are a few things to consider before planting. For instance, your location, climate, soil type, and personal preferences all should be determined to help you plant your best garden.
Choose plants that are suitable for your climate and growing season. For example, if you live in a warm climate with a long growing season, you may be able to grow heat-loving crops like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. If you live in a cooler climate with a shorter growing season, you may need to focus on cold-hardy crops like lettuce, kale, and broccoli.
Different plants thrive in different soil types. Consider the pH level, nutrient content, and drainage of your soil to choose plants that are well-suited to your soil type. You may need to amend your soil with compost or other organic matter to improve its quality.
Most vegetables and herbs require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day to thrive. Choose plants that are well-suited to the amount of sun exposure in your garden.
Consider what types of plants you enjoy eating or using in your cooking. If you love tomatoes, for example, you may want to plant several different varieties of tomatoes in your garden.
Some easy-to-grow vegetables and herbs that are suitable for many gardeners include:
- Tomatoes
- Cucumbers
- Zucchini and other summer squash
- Lettuce and other salad greens
- Peppers
- Herbs like basil, parsley, and thyme
It’s always a good idea to do some research and consult with local experts to determine the best plants for your specific growing conditions.
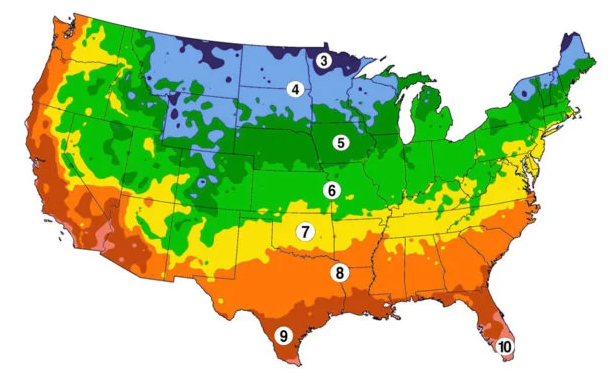
When should I plant my garden?
In general, you should plant your garden when the soil has warmed up and the threat of frost has passed. However, the best time to plant your garden depends on several factors, including location, climate, and types of plants you want to grow. There are two ways that are the most helpful when determining planting time. Using hardiness zones and frost dates.
Here is a general guideline of when to plant by hardiness zone:
- Zone 3: May – June
- Zone 4: May – June
- Zone 5: May – June
- Zone 6: April – May
- Zone 7: April – May
- Zone 8: March – April
- Zone 9: March – April
If you need to find your zone or frost dates or if you want to view a planting guide by state, visit Urban Farmer’s website here. https://www.ufseeds.com/planting-schedules.html
How much water does my garden need?
Most gardens require about 1 inch of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation. However, this amount can vary depending on the type of plants you have, your climate, and the soil type.
To determine how much water you garden needs, you can do a simple soil moisture test. Stick your finger about an inch into the soil. If it feels dry, your garden needs water. If it feels moist, you can hold off on watering for a day or two.
Another method is to use a rain gauge or a container with straight sides placed in your garden to measure how much water your garden receives from rainfall. This will help you determine how much additional water your garden needs to stay healthy.
As a general rule, if the temperatures are dry and hot you will need to water more often. Additionally, if the temperatures are humid and cool you will need to water less often.
How do I prevent pests and diseases in my garden?
- Choose healthy plants: Start with healthy plants that are free from pests and diseases. Inspect the plants carefully before purchasing them.
- Provide proper soil and water conditions: Make sure your plants are planted in soil that drains well and has the right nutrients. Water your plants regularly, but don’t overwater them, as this can lead to root rot.
- Practice good garden hygiene: Keep your garden clean by removing any dead or diseased plant material, and disposing of it properly. This will help prevent the spread of disease.
- Rotate your crops: Rotate your crops from year to year to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
- Use natural pest control methods: Use natural pest control methods, such as companion planting, introducing beneficial insects, and using organic insecticides, to keep pests under control.
- Monitor your garden regularly: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests and diseases, and take action immediately if you notice any problems.
For more information on companion planting, read our article What Plants are the Best for Companion Planting.
How do I fertilize my garden?
In general, to fertilize your garden, you will need to determine the type of fertilizer your plants need, and then apply the fertilizer regularly through the growing season. Here are some basic steps to fertilize your garden:
- Determine the type of fertilizer your plants need: Different plants have different nutrient requirements, so it’s important to determine the type of fertilizer that will best meet the needs of your plants.
- Test your soil: Test your soil to determine its nutrient content and pH level. This will help you determine which nutrients your plants need and how much fertilizer to apply.
- Choose the right type of fertilizer: Choose a fertilizer that contains the nutrients your plants need, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as other micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
- Apply the fertilizer: Apply the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and water your plants after fertilizing to help the nutrients reach the roots.
- Repeat the process: Fertilize your garden regularly throughout the growing season, typically every 4-6 weeks, to ensure that your plants have a steady supply of nutrients.
- Consider organic options: If you prefer to use organic fertilizers, options include compost, manure, and bone meal, which are great for providing slow-release nutrients to your plants.
We like this seaweed fertilizer from Amazon.
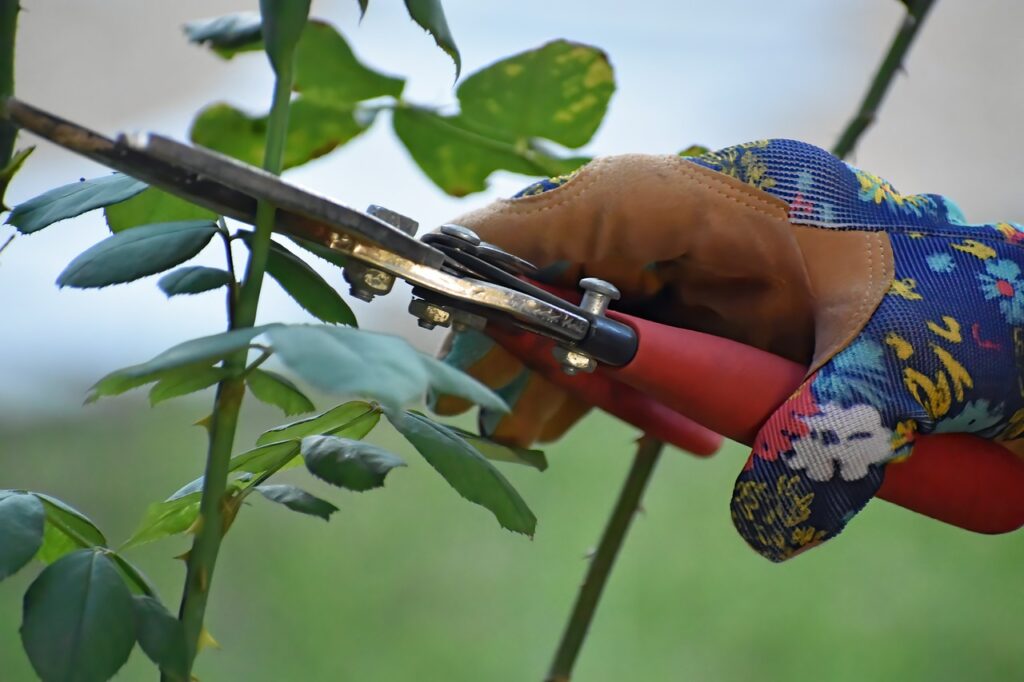

How do I prune my plants and trees?
To prune plants and trees, determine the best time to prune for those plants. The best time to prune depends on the type of plant or tree you’re working with. In general, it’s best to prune in late winter or early spring before new growth appears. However, do research for any specific plant you are wanting to prune.
In order to prune, use sharp, clean pruning shears, loppers, or saws, depending on the size of the branches you’re cutting. Then, remove any dead or damaged branches first, as they can attract pests and diseases. After that, cut back any branches that are overgrown, rubbing against each other, or growing in the wrong direction.
Additionally, you may thin out the canopy of the tree or plant by removing small, weak, or crossing branches to improve air circulation and allow more sunlight to reach the interior. Finally, shape the plant or tree by pruning back the tips of the branches to the desired shape and size. After pruning, step back and evaluate the plant or tree to ensure that it has a balanced and natural shape.
How do I harvest my crops?
The best time to harvest your crops is when they are ripe or fully developed. The timeframe for harvesting is different for all plants. To harvest, use sharp, clean shears to cut the crop as desired. For example, tomatoes may be picked by hand or cut at the stem. Additionally, cabbage can be twisted at the base by hand, or cut.
How do I store my harvest?
To store your harvest, keep vegetables in a cool dark place. Each plant may require different types of storage. For more information, visit our article on food storage, How to Store Fresh Food on a Homestead.
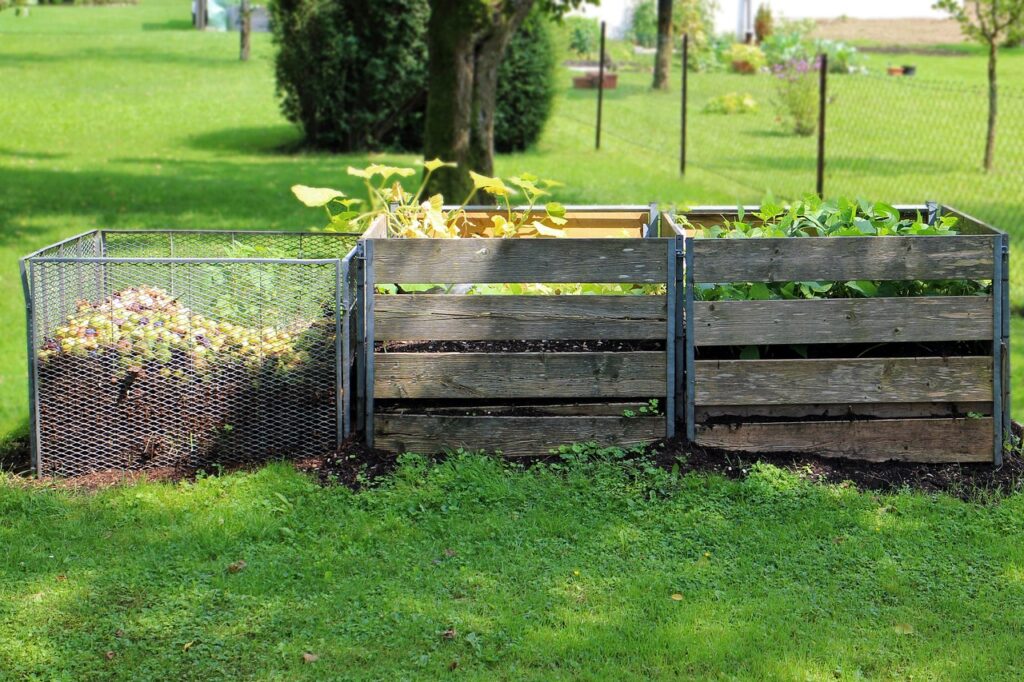

How do I create a compost pile?
In general, a compost pile is made by adding green and brown material into a “pile” or bin that is allowed to decompose. Creating a compost pile is a great way to reduce waste and create a nutrient-rich soil amendment for you garden. Below are some general steps to follow to create a compost pile.
- Choose a location: Choose a location for your compost pile that is convenient, accessible and receives partial sun.
- Collect compostable materials: Collect organic matter, such as fruit and vegetable scraps, yard waste, leaves, and coffee grounds, to use in your compost pile. Avoid using meat, dairy, and oily foods, as they can attract pests and take longer to decompose.
- Prepare the compost bin: Use a compost bin or create a pile on bare ground. If using a bin, choose one that has good air circulation and drainage.
- Layer the compostable materials: Layer the compostable materials in the bin, alternating between “brown” materials, such as dried leaves and wood chips, and “green” materials, such as kitchen scraps and fresh grass clippings. The ideal ratio is 3:1 (brown to green).
- Add water: Add enough water to make the compost pile moist, but not wet.
- Turn the compost: Turn the compost pile every few weeks using a pitchfork or shovel to aerate it and help speed up the decomposition process.
- Monitor the temperature: Check the temperature of the compost pile regularly using a compost thermometer. The ideal temperature range is between 120-150°F (49-66°C).
- Wait for the compost to mature: The compost should be ready in 6-12 months, depending on the size of the pile and the materials used. The finished compost should be dark, crumbly, and have an earthy smell.
While gardening questions are tough to answer, since they are unique to different areas, we hope that we could answer some of them well enough to get you on your way.
Recent Posts
In general, to harvest your own seeds, you must choose mature, healthy plants, allow seeds to dry out, and remove the seeds when they are completely dry. However, this process will look different for...
A guide on how to store and organize seeds for your garden. Vegetables, flowers, herbs, or anything you are wanting to grow. How to Store Your Seeds Proper storage of garden seeds is essential...

